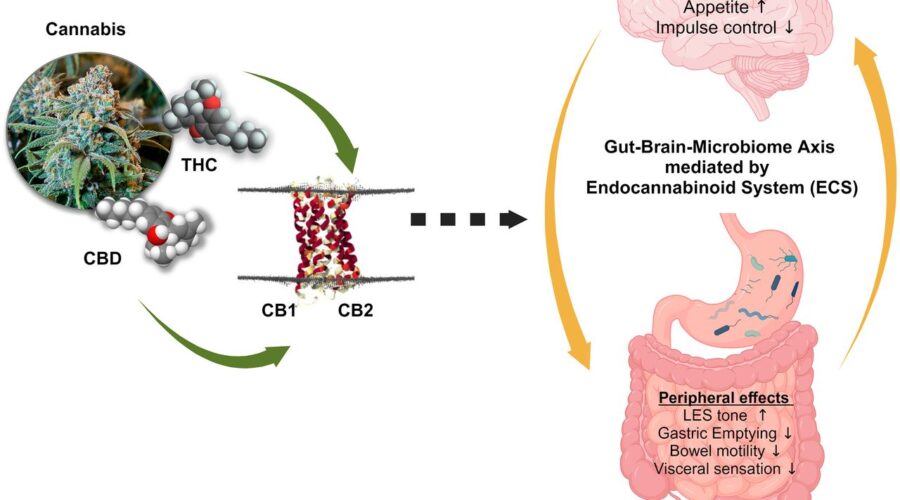
Cannabidiol (CBD), a non-psychoactive cannabinoid from hemp or cannabis, interacts with the endocannabinoid system (ECS) and other pathways to produce therapeutic effects without THC’s “high.” Users and researchers explore CBD for anxiety, pain, inflammation, sleep, and neurological issues.
Discovered in 1940 and researched extensively since the 1990s, CBD gained mainstream attention post-2018 U.S. Farm Bill (legalizing hemp-derived CBD <0.3% THC). As of 2025, the market exceeds USD 10-15 billion, with products like oils, gummies, and topicals widely available. Evidence is strong for epilepsy (FDA-approved Epidiolex), moderate for anxiety/pain, and limited for many claims. Reviews (e.g., 2025 J Cannabis Res) highlight polypharmacology—impacts on serotonin, inflammation, seizures—but note variability by dose, formulation, and individual.
CBD offers promise but isn’t a cure-all; benefits are often modest, with risks like interactions and side effects.
Mechanism of Action
CBD exerts effects via multiple targets:
- Indirect ECS Modulation → Enhances anandamide (no direct CB1/CB2 binding).
- Serotonin 5-HT1A Agonism → Anxiety/mood regulation.
- TRPV1 Activation → Pain/inflammation.
- GPR55 Antagonism → Neuroprotection.
- PPARγ Activation → Anti-inflammatory.
- Ion Channels → Glycine, sodium modulation.
Polypharmacology explains broad effects; no intoxication.
Therapeutic Effects and Evidence
Strong Evidence
- Epilepsy/Seizures Epidiolex reduces seizures in Dravet/Lennox-Gastaut (41% reduction vs. placebo in 2025 Brazilian meta-analysis).
Moderate Evidence
- Anxiety Acute doses (300-600 mg) reduce social anxiety; chronic lower doses help GAD/PTSD symptoms.
- Chronic Pain Modest short-term relief (neuropathic, inflammatory); THC combinations stronger.
- Sleep Improves pain-related sleep; limited for primary insomnia.
- Inflammation Reduces cytokines; potential in arthritis, IBD.
Emerging/Limited Evidence
- Neuroprotection → Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s (preclinical).
- Cancer Support → Symptom relief; anti-tumor preclinical (2025 Chinese review: “substantial promise”).
- Heart Health → Blood pressure reduction.
- Skin → Acne, psoriasis (topical).
2025 reviews: Benefits often short-term; CBD alone less effective for pain than THC combos.
Side Effects and Risks
CBD is well-tolerated but not risk-free:
- Common — Dry mouth, drowsiness, diarrhea, fatigue, appetite changes.
- Dose-Dependent — Higher doses: Liver enzyme elevation (monitor with Epidiolex).
- Interactions — CYP450 inhibition (warfarin, clobazam, antidepressants).
- Other — Low blood pressure, irritability.
Long-term: Limited data; potential male fertility impact (animal studies).
Pregnancy/Breastfeeding: Avoid (developmental risks).
Dosage and Administration
- Start Low → 10-25 mg/day.
- Therapeutic → Anxiety: 300-600 mg acute; chronic pain: 25-100 mg/day.
- Forms → Oils (fast), gummies (convenient), topicals (localized).
Bioavailability: Sublingual > oral > topical.
Conclusion
CBD offers therapeutic effects—strongest for epilepsy, moderate for anxiety/pain/inflammation—with a favorable safety profile compared to many drugs. 2025 evidence supports targeted use but cautions against overhyped claims. Full-spectrum may enhance benefits via entourage. Risks include interactions and variable quality. CBD complements wellness/medical regimens when evidence-based and doctor-guided. Ongoing research refines understanding in this evolving field.
More articles by ZMR Researche:
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/agave-nectar-market
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/foliar-fertilizer-market
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/electric-and-diesel-tractor-market
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/primary-macronutrients-market
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/badminton-equipment-and-facilities-market